-

As 2024 draws to a close, Europe’s energy winter preparedness is a priority. Since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, the EU and its member countries have taken many bold measures to decrease reliance on fossil fuels, accelerate the shift to clean energy and build a more resilient and diversified energy system, with a view to strengthening energy independence and ensuring stable, affordable energy supplies for citizens and businesses.
-

The ongoing war in Ukraine has underscored the EU’s vulnerability to external energy supplies. Europe’s reliance on imported fossil fuels is a liability, not only environmentally but also geopolitically. Prioritising energy efficiency alongside renewable energy and electrification is essential to reducing this dependence. The Energy Efficiency First (EE1st) principle holds the potential to strengthen security and resilience aiming at prioritising energy efficiency wherever it is the most cost-effective solution, ensuring that energy needs are met sustainably and economically.
-

As 2024 draws to a close, Europe’s energy winter preparedness is a priority. Since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, the EU and its member countries have taken many bold measures to decrease reliance on fossil fuels, accelerate the shift to clean energy and build a more resilient and diversified energy system, with a view to strengthening energy independence and ensuring stable, affordable energy supplies for citizens and businesses.
-

Steel remains incredibly relevant and deeply integrated into the modern world. Steel is used extensively in engineering, construction and other applications vital to modern life. The downside is that traditional methods of manufacturing, based upon fossil fuels such as coal, are damaging to the environment as they produce significant quantities of carbon dioxide (CO2). In fact, according to McKinsey & Company1, steel production accounts for about 8% of global emissions. In 2018, every ton of steel produced emitted an average of 1.85 tons of CO2.
-

The cutting-edge, state-backed project at 345 Hudson could be a model for other big buildings sprinting to comply with the city’s building decarbonization law.
-

A call for collective action could help UK pivot away from dependence on Russian fossil fuels
-

Nuclear power is an appropriate choice for replacement of fossil fuels thermal power plants.
-
While the cost of solar power has dropped significantly from the early 2000s, there is still plenty of room for the technology to become cheaper, making it even more attractive as a substitute for fossil fuels.
-

The demand of energy is getting higher, while fossil fuels become scarce. Therefore, investment into the environment, especially in the application of technology to collect, recycle and reuse of the exhaust wastes and heat is an urgent concern.
-
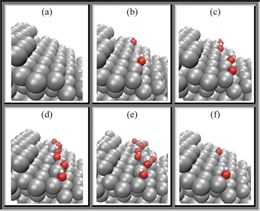
Storage of energy from renewable energy sources is vital to Europe’s energy policy. DTU Energy and partners use atomic modelling to develop a rechargeable zinc-air battery that is able to store large amounts of energy.
-

Across the nation, American businesses, families, and communities are embracing clean, renewable energy that is homegrown, healthy, and can never run out. By finding alternatives to fossil fuels that pollute our air and disrupt our climate, they are showcasing the single most practical way to tackle climate change, starting now.
-

Renewable energy becoming more cost-competitive with fossil fuels isn’t news – as technology improves and more clean power generation comes online, electricity without emissions gets cheaper.
-

Australia not only is one of the largest producers of coal with significant export mainly to China, but is also a big user of fossil fuels, with more than 75% of its 2008/2009 electricity derived from it.
-

As renewable energy technologies become more cost-competitive, the importance of government subsidies is set to decrease to create a sustainable growth platform for both developed and emerging markets, as well as manufacturers
-

In a move that could put wind energy on equal economic footing with traditional fossil fuels, GE (NYSE: GE), Virginia Polytechnic Institute & State University (Virginia Tech), and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), will begin work on a project that could fundamentally change the way wind blades are designed, manufactured and installed.
-

"Our commitment to provide solar power to Haiti will empower local schools and other community facilities, and give students a great place to study and learn while reducing dependency on expensive diesel power and polluting fossil fuels," said Petersen. "I look forward to partnering with the Clinton Foundation as we grow and identify new opportunities to harness the power of the sun by expanding the use of solar power in Haiti."
-

As of 2010, 57% of electricity in Latin America and the Caribbean stems from hydro sources while another 40% comes from thermoelectric power plants using fossil fuels and natural gas. Of the remainder, 2% comes from nuclear stations and 1% from wind, solar and geothermal plants.
-

The study, published online in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), comes on the heels of federal initiatives to wean the United States off fossil fuels by mandating significant increases in ethanol production. The Department of Agriculture forecasts that by 2018, more than one-third of the country's corn harvest will be used to produce ethanol.
-

Innovative green transport systems such as electric tricycles, hybrid jeepneys and electric bicycles have the potential to lessen pollution caused by conventional transportation and the dependency on fossil fuels, according to Senator Edgardo J. Angara.
-

People living in warm climates have been used to using biogas since ages, with even the Assyrians using it to heat their baths 3,000 years ago. But in the colder regions such as Alaska, biogas is harder to produce, since temperatures do not allow for bacteria to ferment the organic waste. However, this problem is about to fade now, as a new type of bacteria has been discovered, and it promises to cut the reliance on fossil fuels for these people big time.



















