Saturday, 07/03/2026 | 14:04 GMT+7
Using the energy of the sun to split water into hydrogen and oxygen gives you access to a completely carbon-free energy source for transportation. But so far, the efficiency of the process has been a bit disappointing, even when using systems called solar-fuel cells—a solar cells immersed in the water it’s splitting.
Now researchers from Eindhoven University of Technology in The Netherlands and the Dutch Foundation for Fundamental Research on Matter (FOM) report in the 17 July issue of Nature Communications that they have improved tenfold the hydrogen producing capacity of a solar fuel cell. The key was to use a photocathode—the electrode that supplies electrons when illuminated by sunlight—made from an array of gallium phosphide nanowires.
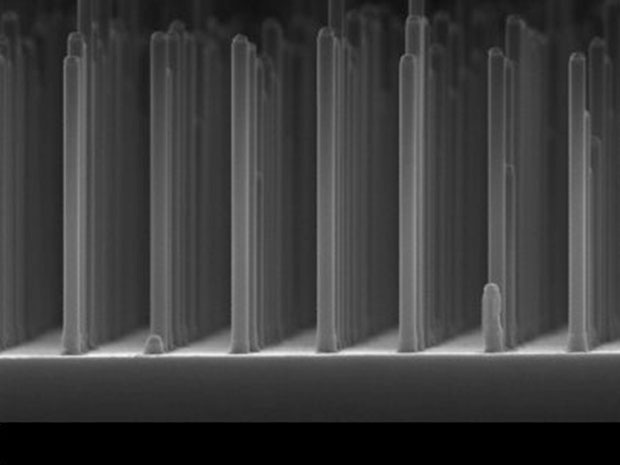
Previously, researchers used flat surfaces of the semiconductor gallium phosphide as the photocathode, but light absorption was low. The GaP nanowires, about 500 nm long and 90 nm thick, increased enormously the surface of the photocathode exposed to light. By adding platinum particles, its catalytic properties improved hydrogen production even more, report the researchers.
At the same time, the nanowires allowed a drastic reduction in the use of GaP material. “For the nanowires we needed ten thousand times less precious GaP material than in cells with a flat surface. That makes these kinds of cells potentially a great deal cheaper,” said Erik Bakkers of Eindhoven University of Technology, as quoted in a press release.
“In addition, GaP is also able to extract oxygen from the water—so you then actually have a fuel cell in which you can temporarily store your solar energy. In short, for a solar fuels future we cannot ignore gallium phosphide any longer,” he added.
Anh Tuan







